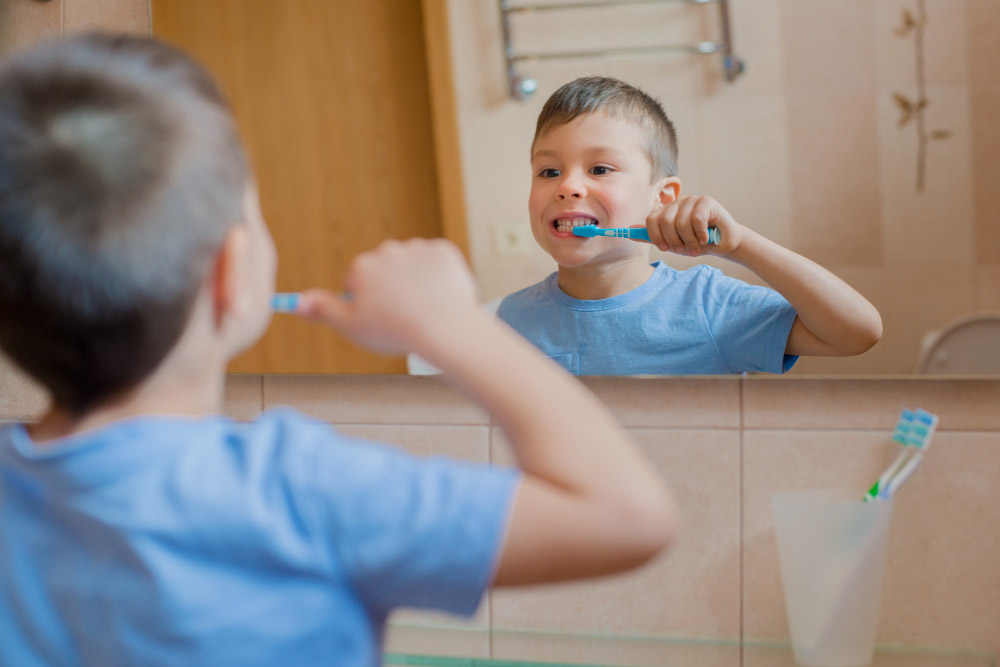
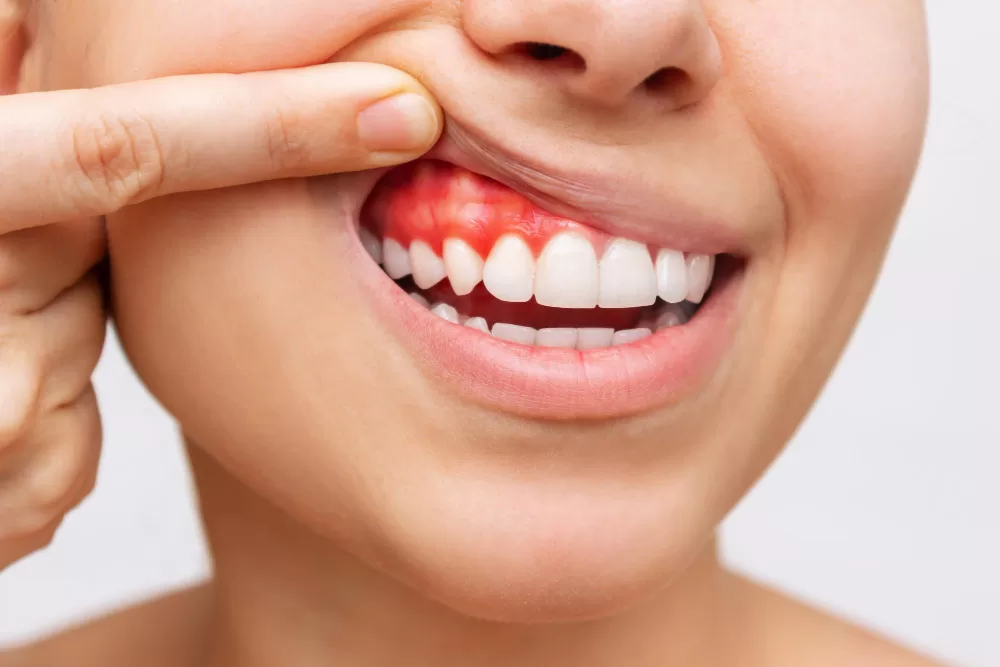
Gum disease, a prevalent concern affecting numerous Australians, manifests in two primary stages: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis, the initial stage, is characterised by mild inflammation and can often be reversed with diligent care. However, if neglected, it may progress to periodontitis, a more severe form impacting the bones and tissues supporting the teeth.
Understanding this condition’s nuances is imperative for maintaining optimal oral health and averting potential complications. This discussion delves into the causes, preventative measures, early indicators, and the correlation between gum health and overall well-being, offering valuable insights for those seeking to fortify their oral health.
Understanding the Causes of Gum Disease
- Gum disease emanates from various factors, with poor oral hygiene standing out as a pivotal contributor. When dental care is neglected, plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—accumulates on teeth, eventually hardening into tartar. This accumulation fosters an environment conducive to gum irritation and disease.
- Moreover, lifestyle choices, particularly smoking, significantly elevate gum disease risks, underscoring the importance of abstaining from such habits. Additionally, underlying health conditions like diabetes can predispose individuals to gum complications, highlighting the necessity of managing such conditions diligently.
- Recognising these risk factors is crucial, as it empowers individuals to implement proactive measures, thereby mitigating the onset and progression of gum disease.
Prevention Strategies
- Preventing gum disease hinges on a robust oral hygiene regimen, encompassing regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, complemented by daily flossing, is fundamental in removing plaque and deterring its transformation into tartar.
- Equally important is adhering to a balanced diet, which bolsters overall oral health. Consuming foods rich in vitamins and minerals, while limiting sugary snacks, can significantly diminish gum disease risks.
- Periodic dental examinations are paramount, as they facilitate early detection and intervention. In Australia, dental professionals adhere to stringent guidelines to ensure comprehensive gum assessments, offering tailored advice and interventions to thwart the onset of gum disease.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
- Vigilance in detecting early gum disease signs is crucial for prompt and effective intervention. Symptoms such as gum redness, swelling, and bleeding, especially during brushing or flossing, warrant immediate attention. Additionally, persistent bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth may signal the onset of gum issues.
- Acknowledging these symptoms is vital, as early intervention can significantly alter the disease’s trajectory, averting its escalation to more severe stages. Australians are encouraged to consult dental practitioners promptly upon observing these signs, ensuring timely and effective care.
The Impact of Gum Disease on Overall Health
- Emerging research underscores a compelling link between gum health and systemic well-being, suggesting that gum disease may influence, or be influenced by, broader health conditions. For instance, individuals with gum disease exhibit a heightened risk of cardiovascular complications, underscoring the importance of maintaining optimal gum health.
- Moreover, gum disease is associated with diabetes management challenges, with reciprocal influences highlighting the intricate connections between oral health and broader physiological processes. Respiratory conditions also exhibit associations with gum health, further exemplifying the systemic implications of oral diseases.
- In light of these insights, it is evident that gum health transcends mere oral well-being, bearing significant implications for overall health. Consequently, adopting a holistic approach to oral hygiene, cognisant of its broader health ramifications, is imperative for individuals aiming to safeguard their health comprehensively.
Professional Dental Care for Gum Health
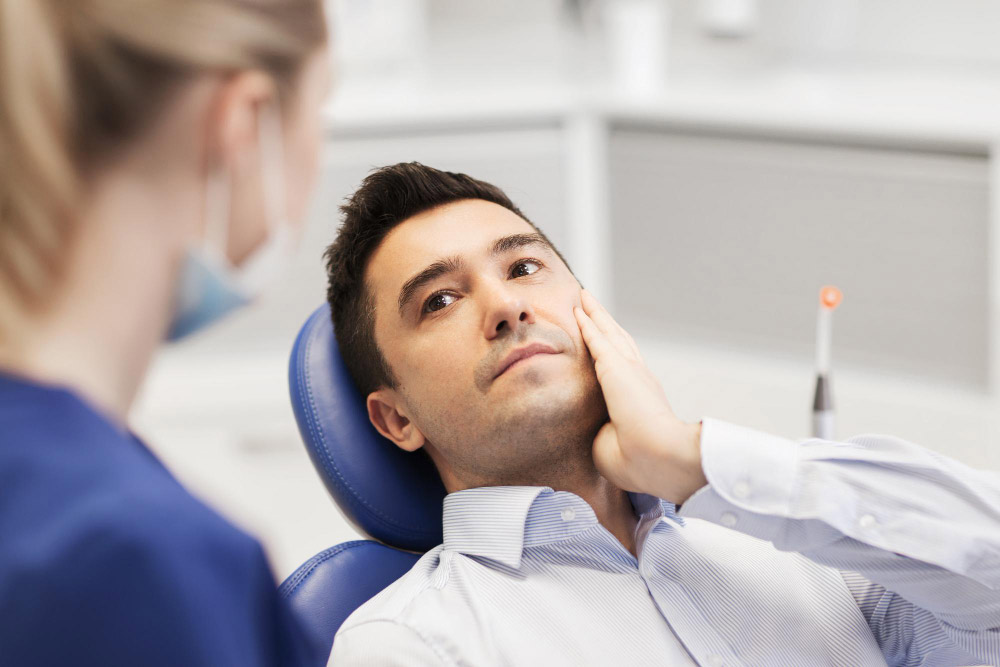
- Securing professional dental care is a cornerstone of maintaining optimal gum health. In Australia, dentists employ a comprehensive approach to evaluate and manage gum health, ensuring that any signs of disease are promptly addressed. Regular dental visits allow for the meticulous removal of plaque and tartar, which are pivotal in preventing gum disease progression.
- During these visits, dental professionals conduct thorough examinations, utilising advanced diagnostic tools to assess gum health meticulously. Such evaluations are crucial in detecting gum disease in its nascent stages, facilitating early intervention and improving prognostic outcomes. Australian dental practices adhere to rigorous standards, ensuring that patients receive top-tier care informed by the latest research and best practices.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
- When gum disease is identified, several non-surgical treatment options can be employed, depending on the condition’s severity. One fundamental non-surgical approach is scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning procedure that meticulously removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line. This treatment is vital in eliminating the bacteria responsible for gum disease, thereby curbing its progression.
- Adjunctive therapies, such as the application of antimicrobial agents, may also be recommended to enhance treatment efficacy. These interventions are pivotal in managing gum disease, aiming to restore gum health and prevent the necessity for more invasive procedures.
- Australian dental practitioners are adept at tailoring these non-surgical treatments to individual patient needs, ensuring that each person receives optimal care that aligns with their specific condition and health objectives.
Surgical Treatment Options
- In instances where gum disease has advanced, necessitating intervention beyond non-surgical means, various surgical treatments are available. These procedures, executed with precision and care by skilled dental surgeons, are designed to restore gum health and prevent further damage.
- Flap surgery, for instance, involves making incisions in the gum to provide access to the roots for better scaling and root planing. For patients experiencing bone loss, procedures such as bone grafting may be recommended to regenerate lost bone and tissue, supporting overall dental health and stability.
- Guided tissue regeneration is another surgical option, employing biocompatible materials to encourage the body’s natural healing processes to regenerate bone and tissue. These advanced surgical treatments, while more involved, offer significant benefits in managing advanced gum disease, ultimately aiming to preserve natural teeth and maintain oral health.
Recovery and Aftercare Following Treatment
Following any gum disease treatment, be it non-surgical or surgical, adherence to prescribed aftercare protocols is essential for successful outcomes. Patients are advised to maintain meticulous oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, to support healing and prevent recurrence.
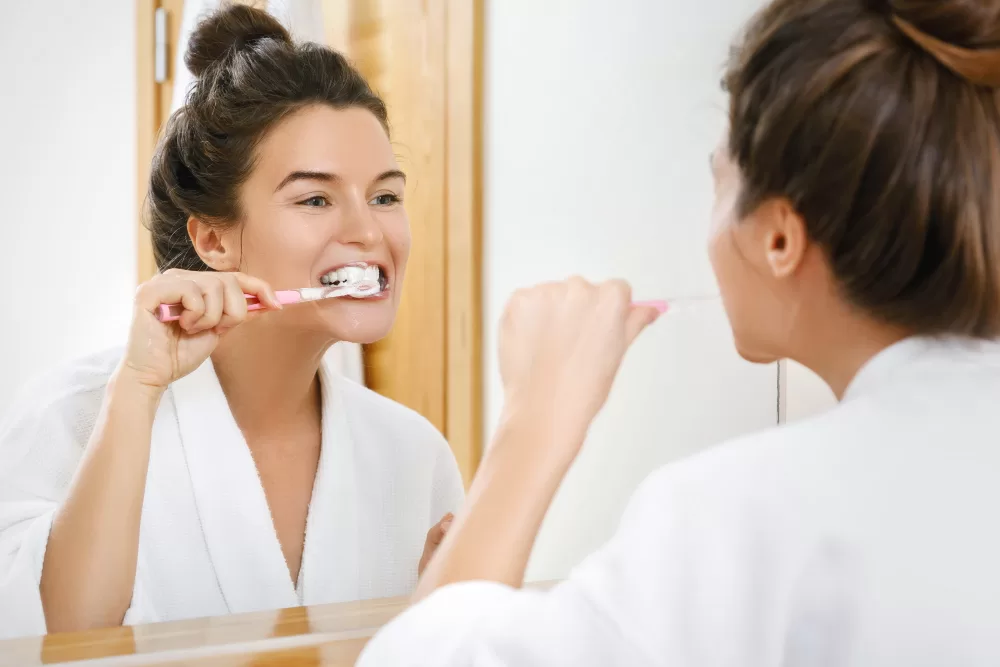

- Dental professionals will provide comprehensive aftercare instructions, tailored to the specific treatment undergone. These may include recommendations on diet, activity limitations, and oral hygiene practices, all aimed at fostering optimal healing and preventing future gum issues.
- Regular follow-up appointments are crucial, allowing dentists to monitor healing progress and make any necessary adjustments to the patient’s care plan. These appointments offer an opportunity to address any concerns and ensure that the patient’s recovery is on track, reinforcing the collaborative nature of dental care in achieving lasting oral health.
Emphasising Early Intervention and Prevention
- The trajectory of gum disease can often be altered significantly through early detection and intervention. Australians are encouraged to remain vigilant about their oral health, seeking professional care at the first sign of gum issues. By doing so, individuals can significantly improve their chances of reversing gum disease and avoiding more severe health complications.
- Preventive measures, such as regular dental check-ups and maintaining excellent oral hygiene, are paramount in thwarting the onset of gum disease. By adopting a proactive approach to oral health, individuals can safeguard their gums, teeth, and overall well-being, underscoring the profound connection between oral health and general health.
- In closing, while gum disease poses significant risks, the opportunities for prevention and effective treatment are robust, particularly when individuals engage actively in their oral health care. For those seeking expert dental care in Fairfield, Victoria, “Care For Smiles” offers a comprehensive range of services to support optimal oral health, embodying a commitment to patient-centred care and excellence in dental practice.
- By partnering with trusted dental professionals and adopting a diligent approach to oral hygiene, individuals can navigate the challenges of gum disease, securing not only their oral health but also contributing positively to their overall health and quality of life.
FAQs About Gum Disease:
1. What is gum disease and how is it caused?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an inflammatory condition affecting the gums and, in severe cases, the surrounding bone. It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of food debris, bacteria, and saliva. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, exacerbating gum inflammation and leading to the progression of gum disease.
2. What are the early signs of gum disease?
The early signs of gum disease include red, swollen, or tender gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. Other symptoms include persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth. Recognising these early signs is crucial for seeking timely dental intervention and preventing the progression of the disease.
3. How can I prevent gum disease?
Preventing gum disease involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also vital, as they help remove plaque and tartar that can contribute to gum disease. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet and avoiding tobacco, can further reduce the risk of gum disease.
4. What are the treatment options for gum disease?
Treatment options for gum disease vary depending on the severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatments include professional dental cleaning, scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), and antimicrobial treatments. In more advanced cases, surgical treatments such as flap surgery, bone grafting, or guided tissue regeneration may be necessary to restore gum health.
5. Can gum disease affect my overall health?
Yes, gum disease can impact overall health. Research has linked severe gum disease to various systemic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. The inflammation associated with gum disease is believed to play a role in these associations, underscoring the importance of maintaining good oral health for overall well-being.
6. What should I do if I suspect I have gum disease?
If you suspect you have gum disease, it’s important to schedule an appointment with a dentist promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the disease from progressing and reduce the risk of associated health complications. Your dentist can assess your gum health, recommend appropriate treatment, and provide guidance on improving your oral hygiene practices to support gum health.